Cupping
Cupping is a therapy in which a jar is attached to the skin surface to cause local congestion through the negative pressure created by introducing heat in the form of an ignited material. In the ancient times in China, the cupping method was called “horn method.”
1. Type of Jars
There are a great variety of jars, but the commonly used are as follows and the images of the different cups show how the cups change according to the new material available.






1) Bamboo Jar:
Cut down a section of bamboo 3-7cm in diameter and 8-10cm in length, forming a cylinder shaped as a drum. One end is used as the bottom, and the other as the opening. The rim of the jar is light, economical, easy to make and available in many places.
2) Glass Cup:
Since the glass cup is transparent, the local congestion at the site for moxibustion can be seen so as to control the treatment.
3) Bio-ceramic Cup:
This seramic cup contains Germanium made under hight temperature-1400°C- so that it gives off the far-infrared heat to the body. when this cupping combines with the infrared heat, cups keep the heat longer and the heat penetrates deeper.
2. Indications
The cupping method has the function of warming and promoting the free flow of qi and blood in the meridians, dispelling cold dampness, diminishing swellings and pains.
In clinics, the cupping method is mainly used to treat Bi syndrome caused by wind dampness, such as pain of the low back, shoulder, and leg, gastrointestinal disorders such as stomachache, vomiting, and diarrhea, and lung diseases such as cough and asthma.
The cupping method combined with bloodletting is suitable to treat acute sprains accompanied by blood stasis.
The animal horn was used to dispel pus. Along with continual development in clinical practice, the materials for making jars and the methods have been greatly improved. The range of indications has been expanded, since this method is simple and the therapeutic effect is good. This therapy was attracted with great attention and applied in a large scale by the broad masses, and also used as an auxiliary method of acupuncture and moxibustion.
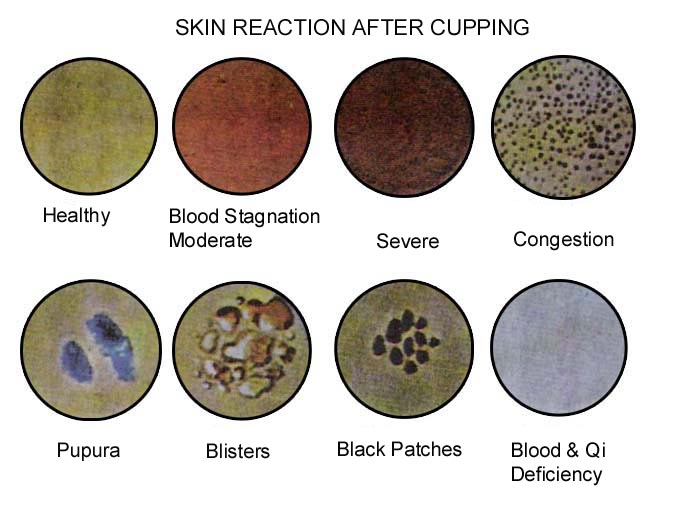
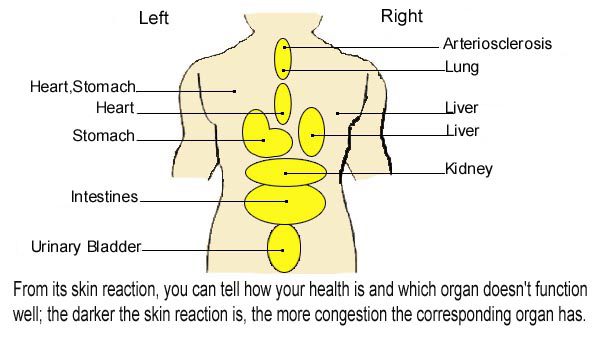
3. Skin Reaction Afterwards and Corresponding Organs